cloud service models#
Core cloud service models#
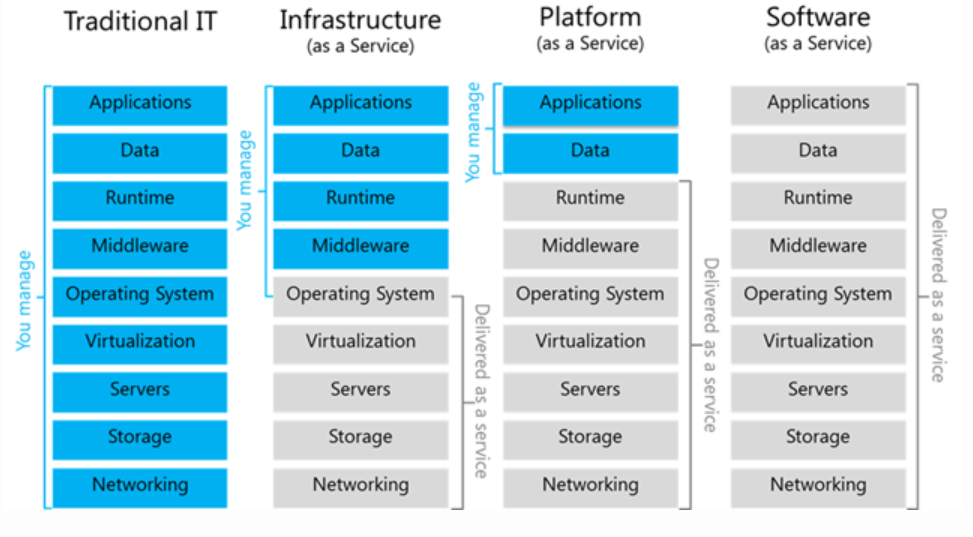
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)#
Definition: The cloud provider manages the physical hardware, and the customer can configure virtual machines, networks, and storage. Customers have control over the OS and the software stack above it.
- AWS: Amazon EC2
- Azure: Virtual Machines
- Google Cloud: Compute Engine
- Open Source: OpenStack
Platform as a Service (PaaS)#
Definition: Goes a step further than IaaS by also managing the operating systems, middleware, and runtime environments. Customers focus on deploying and managing their applications.
- AWS: Elastic Beanstalk
- Azure: Web Apps
- Google Cloud: App Engine
- Open Source: Cloud Foundry
Software as a Service (SaaS)#
Definition: The provider manages everything, and the customer uses the software over the internet, typically on a subscription basis. The customer doesn’t manage or control the underlying infrastructure.
- AWS: No specific example, but AWS hosts many SaaS applications.
- Azure: Office 365
- Google Cloud: Google Workspace
- Open Source: Nextcloud (for certain applications)
Specialized cloud service models#
Kubernetes as a Service (KaaS)#
Definition: Provides managed Kubernetes clusters, handling the control plane and leaving the data plane and applications to the customer.
- AWS: Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Azure: Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Google Cloud: Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Open Source: There are open-source tools for managing Kubernetes, like Rancher, but KaaS is typically a cloud provider offering.
Containers as a Service (CaaS)#
Definition: The provider manages the orchestration of containers, including both the control and data planes. Customers provide and manage the container images.
- AWS: Fargate
- Azure: Container Instances
- Google Cloud: Cloud Run
- Open Source: Docker Swarm (for orchestration)
Functions as a Service (FaaS)#
Definition: Allows customers to run code in response to events without managing servers. The provider handles the infrastructure, scaling, and event triggering.
- AWS: Lambda
- Azure: Functions
- Google Cloud: Cloud Functions
- Open Source: OpenFaaS
No-Code as a Service#
Definition: Enables building applications without writing code, using visual development environments. The provider manages everything, and the customer configures the application logic.
- AWS: Honeycode
- Azure: Power Apps
- Google Cloud: AppSheet
- Open Source: There are various no-code platforms, but not in the open-source domain with cloud-level integration like the above.
Communications as a Service (CaaS)#
Definition: A cloud-based solution that allows businesses to outsource their communication needs, including VOIP, instant messaging, video conferencing, and more.
- AWS: Amazon Chime
- Azure: Azure Communication Services
- Google Cloud: Does not offer a direct CaaS solution but Google Voice and Google Meet can be considered part of Google Workspace’s broader communication offerings.
- Open Source: Asterisk, an open-source framework for building communications applications, can serve as a foundation for a CaaS solution.
Desktop as a Service (DaaS)#
Definition: Provides virtual desktops over the internet, allowing users to access their desktop environments from anywhere.
- AWS: Amazon WorkSpaces
- Azure: Windows Virtual Desktop
- Google Cloud: Google Cloud’s Desktop as a Service is not directly offered, but Google Cloud VMware Engine can facilitate virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) solutions.
- Open Source: Apache Guacamole is an open-source clientless remote desktop gateway that supports standard protocols like VNC and RDP.
Database as a Service (DBaaS)#
Definition: A cloud service model that provides users with access to databases without the need for setting up physical hardware, installing software, or configuring for performance.
- AWS: Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service)
- Azure: Azure SQL Database
- Google Cloud: Cloud SQL
- Open Source: MongoDB Atlas can be considered an open-source DBaaS, even though it’s offered by MongoDB Inc. as a cloud service. PostgreSQL and MySQL can be self-hosted in a cloud environment to create a DBaaS-like experience.
Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS)#
Definition: Offers organizations the ability to recover their critical IT infrastructure and data after a disaster. This service minimizes downtime and data loss.
- AWS: AWS Disaster Recovery
- Azure: Azure Site Recovery
- Google Cloud: Does not have a direct DRaaS offering but supports disaster recovery planning through its various services.
- Open Source: ReaR (Relax-and-Recover) can be used in conjunction with cloud services for creating disaster recovery solutions.
Backend as a Service (BaaS)#
Definition: Simplifies the development of backend web services and mobile application backend, providing features like database management, cloud storage, and user authentication.
- AWS: AWS Amplify
- Azure: Azure Mobile Apps
- Google Cloud: Firebase
- Open Source: Parse Platform (an open-source version of the Parse BaaS that was shut down by Facebook, now maintained by the community).
Security as a Service (SECaaS)#
Definition: Offers security management by cloud providers. Services can include anti-virus, anti-malware, intrusion detection, and security event management.
- AWS: AWS Shield for DDoS protection
- Azure: Azure Security Center
- Google Cloud: Google Cloud Security Command Center
- Open Source: OpenVAS for vulnerability scanning is an example of how open-source tools can be integrated into a security service model.
Identity as a Service (IDaaS)#
Definition: Provides identity and access management services in the cloud. This can include single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and user management.
- AWS: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Azure: Azure Active Directory
- Google Cloud: Google Cloud Identity
- Open Source: Keycloak offers open-source IDaaS capabilities with SSO, MFA, and social login.
Analytics as a Service (AaaS)#
Definition: Offers data analytics and business intelligence tools in the cloud, enabling organizations to analyze and visualize their data without managing the underlying infrastructure.
- AWS: AWS Analytics
- Azure: Azure Synapse Analytics
- Google Cloud: Google BigQuery
- Open Source: Apache Superset can serve as an open-source alternative for data visualization and business intelligence, although it’s not a cloud service per se but can be hosted on any cloud platform.
Machine Learning as a Service (MLaaS)#
Definition: Provides machine learning tools as part of the cloud computing services, allowing users to leverage artificial intelligence without the high cost or complexity of developing and maintaining their own AI infrastructure.
- AWS: Amazon SageMaker enables developers to build, train, and deploy machine learning models quickly.
- Azure: Azure Machine Learning offers a comprehensive environment for building, training, and deploying machine learning models.
- Google Cloud: AI Platform makes it easy for machine learning developers, data scientists, and data engineers to take their ML projects from ideation to deployment and production.
- Open Source: TensorFlow and PyTorch are open-source machine learning libraries that, while not services themselves, can be run on any cloud provider to create a custom MLaaS.
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS)#
Definition: A suite of cloud services enabling development, execution, and governance of integration flows connecting any combination of on-premises and cloud-based processes, services, applications, and data within individual or across multiple organizations.
- AWS: AWS AppFlow enables secure, automated data flows between AWS services and SaaS applications.
- Azure: Azure Logic Apps provides a cloud service that helps you schedule, automate, and orchestrate tasks, business processes, and workflows when you need to integrate apps, data, systems, and services across enterprises or organizations.
- Google Cloud: Apigee Integration is Google CloudΓÇÖs solution for creating and managing API-first, integration-led connectivity.
- Open Source: Apache Camel is an open-source integration framework that empowers you to integrate various systems consuming or producing data.
Edge Computing as a Service (ECaaS)#
Definition: Extends cloud computing services to the edge of the network, closer to the source of data. This model facilitates faster processing and response times by reducing the distance data needs to travel.
- AWS: AWS Wavelength brings AWS services to the edge of the network, minimizing latency to connect to an application from a mobile device.
- Azure: Azure Edge Zones extend Azure services to the edge, with seamless integration and connectivity to Azure for faster, secure, and more reliable experiences.
- Google Cloud: Google Anthos for Telecom, while more of a hybrid cloud platform, can be seen as part of Google’s approach to edge computing, enabling telecom operators to run applications wherever it makes the most sense.
- Open Source: EdgeX Foundry, a project under the LF Edge umbrella, is building a common open framework for IoT edge computing.